Your Second derivative test example images are ready. Second derivative test example are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Second derivative test example files here. Download all free images.
If you’re searching for second derivative test example images information related to the second derivative test example topic, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site frequently provides you with hints for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
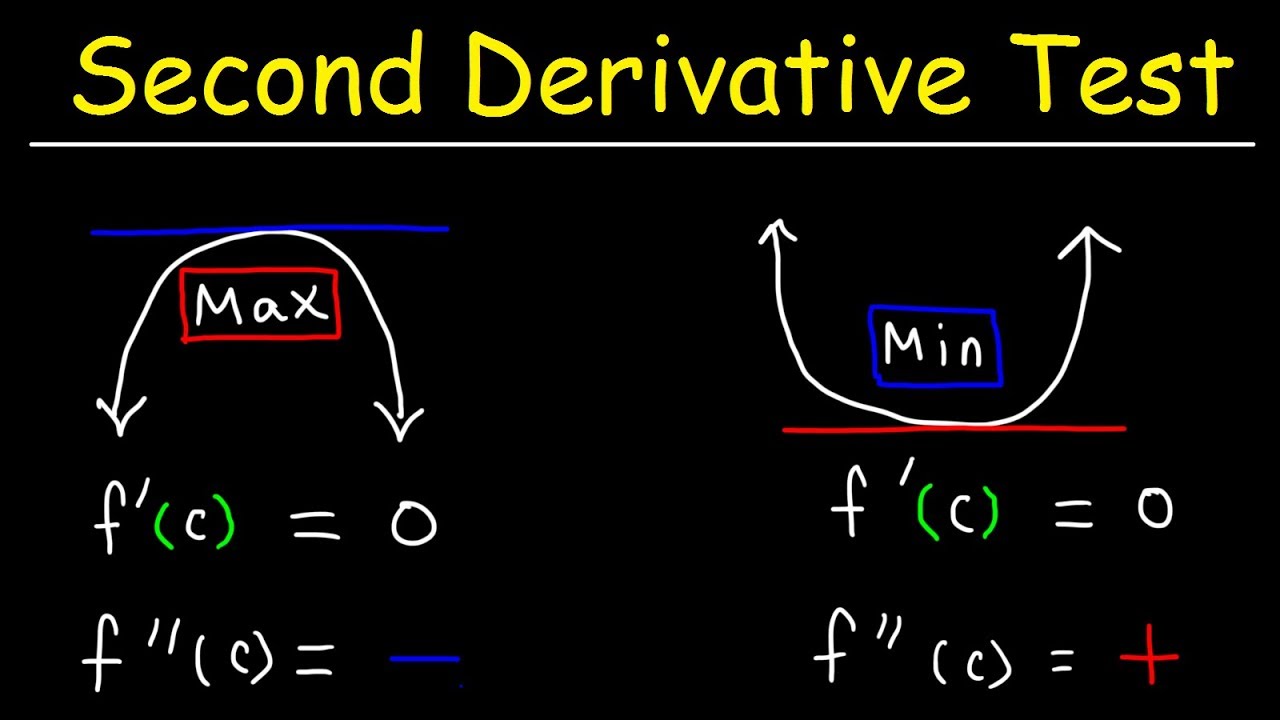
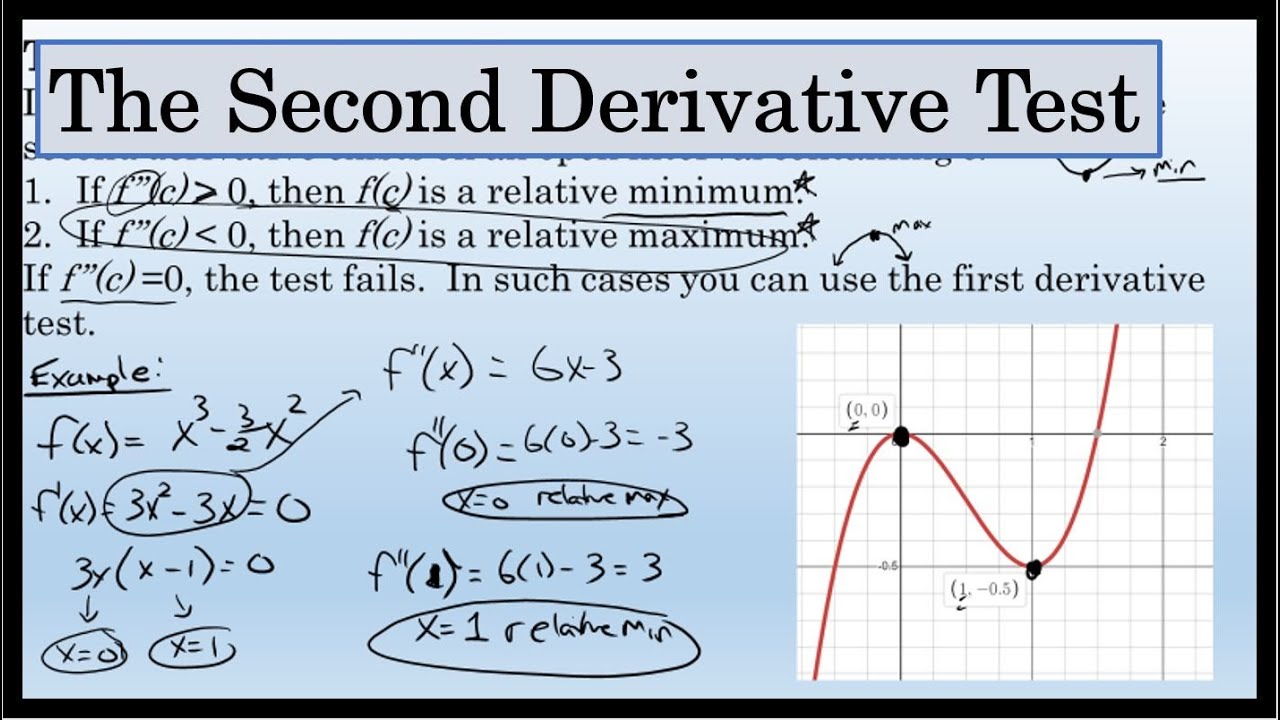
Second Derivative Test Example. Show Next Step Example 2 Let f x - x3 3 x2 3 x. Find the critical points of w 12x2 y3 12xy and determine their type. Using the Product Rule we get. If f x 0 then f c is a relative maximum.

If playback doesnt begin. As is indicated in the third option of the test if a critical number c is also a subcritical number then the second derivative test cannot help determine whether or not there is a max or min at c. The Second Derivative Test Let f be a twice differentiable function near c such that f c 0. Second Derivative Test To Find Maxima Minima. Now lets move to more variables where we have fx 0 Δx fx 0 HΔx near the critical point. If f x 0 then f c is a relative maximum.
It is also known as the delta method.
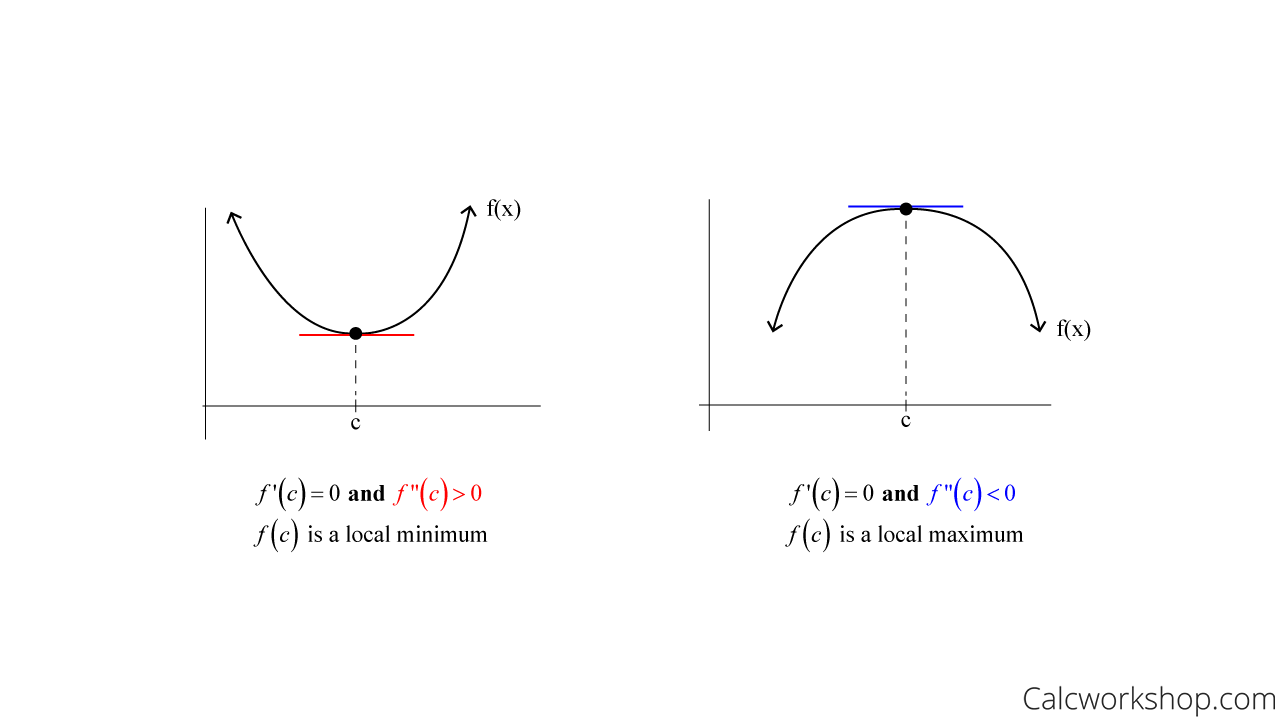
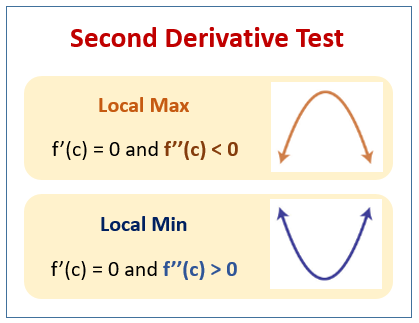
If f c 0 then f x has a relative maximum at x c. Lets test the intervals to either side of 1. Example 2 Determine the regions in which the following function is concave upward or downward. Mathematically if y fx y f x Then dy dx d y d x f x Now if f x is differentiable then differentiating dy dx d y d x again wrt. Then If f x 0 then f c is a relative minimum. Definition of First Principles of Derivative.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Examples of using the second derivative to determine where a function is concave up or concave down. F 6x 2 12x. Derivative by the first principle refers to using algebra to find a general expression for the slope of a curve. If possible use the second derivative test to determine if each critical point is a maximum a minimum or neither. This is negative so according to the second partial derivative test the point is a.
 Source: copingwithcalculus.com
Source: copingwithcalculus.com
Now that we have the second derivative we need to check for critical values. 2 SECOND DERIVATIVE TEST Example 1. Examples of using the second derivative to determine where a function is concave up or concave down. Using the Product Rule we get. The third derivative f is the derivative of the second derivative.

F 3x 5 5x 3 3 15x 4 15x 2 15x 2 x-1x1 Step 2. Now that we have the second derivative we need to check for critical values. We can solve a second order differential equation of the type. To find f x we differentiate f x. Show Next Step Example 2 Let f x - x3 3 x2 3 x.

Second partial derivative test example part 1 - YouTube. When the second derivative test fails doesnt work because the second derivative equals 0 we study the sign of the first derivative at the stationary point. Find the critical points of w 12x2 y3 12xy and determine their type. The derivative of a displacement function is velocity. There is no x-value at which the second derivative can equal 0 however the function does not exist at x 1 so that will be our only critical value.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Then i Local Minima. Using the Product Rule we get. Find the critical points of w 12x2 y3 12xy and determine their type. A w xx 24 2 w x 24x 2 12y B w xy 12 w y 3y 12x C w y y 6y To find the critical points we solve simultaneously the equations w x 0 and w y 0. But using the second derivative test if we take the second derivative and if we see that the second derivative is indeed less than zero then we have a relative maximum point.
 Source: calcworkshop.com
Source: calcworkshop.com
Find the 2nd derivative of 2x 3. Now that we have the second derivative we need to check for critical values. Second Derivative Test Examples BACK NEXT Example 1 Let f x xex. F 2x 3 6x 2 Step 2. If our second derivative is greater than zero then we are in this situation right here were concave upwards.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
For example we use the second derivative test to determine the maximum minimum or the point of inflexion. Let f x x 4 - 4x 3 Then f x 4x 3 - 12x 2 which is zero at x 0 and x 3. Where the slope is zero thats the. This is negative so according to the second partial derivative test the point is a. Find the critical points of w 12x2 y3 12xy and determine their type.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
If our second derivative is greater than zero then we are in this situation right here were concave upwards. And this is a parabola that opens upward making the vertex a minimum if b is positive and a max if b is negative. Definition of First Principles of Derivative. This is negative so according to the second partial derivative test the point is a. Further the second derivative test can be supposed to be useful in the following example situations.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Find the concavity of fx x3 - 3x2 using the second derivative test. Find the 2nd derivative of 2x 3. Second Derivative Test Examples BACK NEXT Example 1 Let f x xex. Then so this is a situation that we started with right up there. Find the 2nd derivative of 3x 5 5x 3 3.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
A w xx 24 2 w x 24x 2 12y B w xy 12 w y 3y 12x C w y y 6y To find the critical points we solve simultaneously the equations w x 0 and w y 0. Second partial derivative test example part 1 - YouTube. The derivative is a measure of the instantaneous rate of change which is equal to. Derivative by the first principle refers to using algebra to find a general expression for the slope of a curve. We get w x 0 y 2x x y 0 0 4x2 4x x.
 Source: cuemath.com
Source: cuemath.com
Where the slope is zero thats the. Then If f x 0 then f c is a relative minimum. If playback doesnt begin. To apply the second derivative test we plug in each of our stable points to this expression and see if it becomes positive or negative. We calculate the partial derivatives easily.
 Source: onlinemathlearning.com
Source: onlinemathlearning.com
Know the definition of the derivative test. Let f x x 4 - 4x 3 Then f x 4x 3 - 12x 2 which is zero at x 0 and x 3. As is indicated in the third option of the test if a critical number c is also a subcritical number then the second derivative test cannot help determine whether or not there is a max or min at c. D2y dx2 Ptdy dx Qy ft Undetermined Coefficients that work when f x is a polynomial exponential sine cosine or a linear combination of those. Show Step-by-step Solutions Second Derivative Test for Relative Maximum and Minimum The second derivative test is useful when trying to find a relative maximum or minimum if a function has a first derivative that is zero at a certain point.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The profit from a grove of orange trees is given by the expression Px ax bx 2 cx 3 d where a b are constants and x is the number of mango trees per acre. To apply the second derivative test we plug in each of our stable points to this expression and see if it becomes positive or negative. Know the definition of the derivative test. If f c 0 then f x has a relative minimum at x c. Where the slope is zero thats the.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
D2y dx2 Ptdy dx Qy ft Undetermined Coefficients that work when f x is a polynomial exponential sine cosine or a linear combination of those. When it works the second derivative test is often the easiest way to identify local maximum and minimum points. If f x 0 then use the first derivative test. F 6x 2 12x. Variation of Parameters which is a little messier but works on a wider range of functions.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Find the critical points of w 12x2 y3 12xy and determine their type. Hence we have the second derivative test. Then i Local Minima. Take the derivative of your answer from Step 1. This is negative so according to the second partial derivative test the point is a.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Lets test the intervals to either side of 1. F 6x 2 12x. If the derivative term is zero we get the graph of a bh2 near fx. In such cases we must fall back on one of the previous tests. Then so this is a situation that we started with right up there.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
We get w x 0 y 2x x y 0 0 4x2 4x x. Mathematically if y fx y f x Then dy dx d y d x f x Now if f x is differentiable then differentiating dy dx d y d x again wrt. Find the concavity of fx x3 - 3x2 using the second derivative test. Then so this is a situation that we started with right up there. Second partial derivative test example part 1.
 Source: copingwithcalculus.com
Source: copingwithcalculus.com
Know the definition of the derivative test. If our second derivative is greater than zero then we are in this situation right here were concave upwards. Find the 2nd derivative of 2x 3. If fx x cos x find f x. If playback doesnt begin.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title second derivative test example by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






