Your Rank size rule example images are ready. Rank size rule example are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Rank size rule example files here. Find and Download all free photos.
If you’re searching for rank size rule example images information linked to the rank size rule example interest, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our site frequently provides you with hints for seeing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Rank Size Rule Example. The size of a particular town can be predicted by observing its rank and the size of the largest city in the area. The Rank-Size Rule If all cities in a country are placed in order from the largest to the smallest each one will have a population half the size of the preceding city. Butler 2005 According to Waugh 2010 the rank size rule is a model that attempts. The major city population is 3547 million and the.
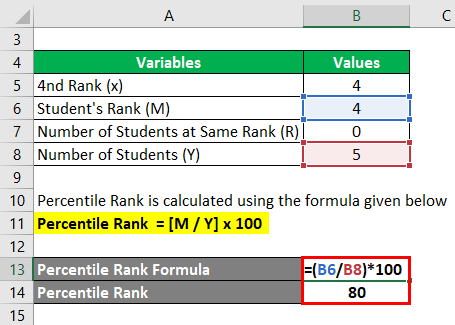 Percentile Rank Formula Calculator Excel Template From educba.com
Percentile Rank Formula Calculator Excel Template From educba.com
This rule predicts that if the settlements in a country are ranked by population size the population of a settlement ranked n will be 1nth of the size of the largest settlementWhen settlement size is plotted against rank on normal graph paper a concave curve results. 125 or to put it in much simpler words. Most developed nations follow this rule unless they have a primate city. The rank-size rule does not imply that the ranking of a city directly relates itself to the population of a city. This is also known as the rank-frequency distribution when the source data are from a frequency distribution. The Rank Size Rule inspired by Zipfs Law Applied to Distribution of Cities 1935 says if all cities in a country are placed in order from the largest to the smallest each one will have a population 1nth the size of the largest city in the country.
Rank 1 Largest City Rank 2 ½ the number of people as Rank 1 city Rank 3 13 the number of people as Rank 1 city.
The Rank Size Rule inspired by Zipfs Law Applied to Distribution of Cities 1935 says if all cities in a country are placed in order from the largest to the smallest each one will have a population 1nth the size of the largest city in the country. According to the rank-size rule there should be a larger number of small cities than bigger cities. The size of a particular town can be predicted by observing its rank and the size of the largest city in the area. The Rank Size Rule is a theory of how large the population of the different major cities are in a country should be. The Rank-Size Rule If all cities in a country are placed in order from the largest to the smallest each one will have a population half the size of the city before it. The rank size rule states that the largest city in a given country will have of the population of the largest city in that country.
 Source: towardsdatascience.com
Source: towardsdatascience.com
The principle that many things all over the world for example the sizes of cities or businesses. Theoretically there should be. If we estimate this rule for all cities in a region or country and transform everything to a linear form the relationship can be. Zipfs law applied to distribution of cities 1935. A pattern of settlements in a country such that the nth large.
 Source: esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Places we test the hypothesis that the population of a citys second-largest city should be half the size of that it. The population of urban settlements towns cities will be inversely proportional to the rank in the urban Hierarchy. This rule predicts that if the settlements in a country are ranked by population size the population of a settlement ranked n will be 1nth of the size of the largest settlementWhen settlement size is plotted against rank on normal graph paper a concave curve results. 125 or to put it in much simpler words. The rank-size rule is a theory.
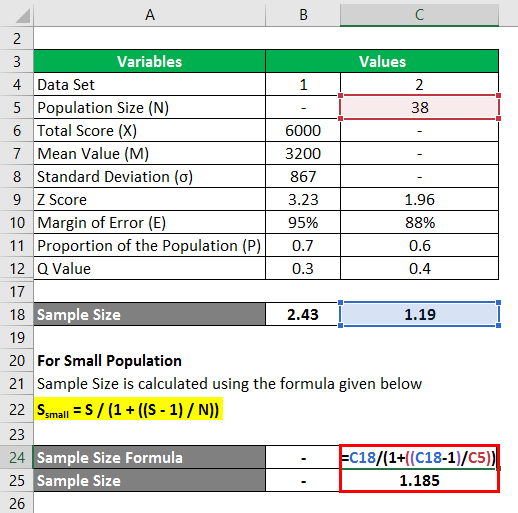 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
125 or to put it in much simpler words. Rank-size distribution is the distribution of size by rank in decreasing order of size. The size of a particular town can be predicted by observing its rank and the size of the largest city in the area. Rank-Size rule in geography UPSC. The pattern of the rank-size rule was.
 Source: juran.com
Source: juran.com
The settlements within a defined area are ranked in descending order according to the size of their population. A larger threshold provides more goods and services a place f. People by the rank of the second-largest city 2. Assumptions The 2nd ranked city will have 12 the population of the 1st The 3rd ranked city will. Rank-size distribution is the distribution of size by rank in decreasing order of size.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
The Rank-Size Rule. Most developed nations follow this rule unless they have a primate city. This theoretical guide the rank-size rule predicts a population of 57500 for Quebec City not far off from the actual figure recorded at the time 60000. The Rank-Size Rule. It is the concept of explaining the hierarchy of urban settlement at a place.
 Source: geographyfieldwork.com
Source: geographyfieldwork.com
The Rank Size Rule is a theory of how large the population of the different major cities are in a country should be. The rank size rule is an empirical regularity. Places we test the hypothesis that the population of a citys second-largest city should be half the size of that it. The Rank-Size Rule If all cities in a country are placed in order from the largest to the smallest each one will have a population half the size of the preceding city. In an ordered set of.
 Source: newellta.weebly.com
Source: newellta.weebly.com
A pattern of settlements in a country such that the nth largest settlement is 1n the population of the largest settlement. Places we test the hypothesis that the population of a citys second-largest city should be half the size of that it. A pattern of settlements in a country such that the nth large. The principle that many things all over the world for example the sizes of cities or businesses. The Rank Size Rule is a theory of how large the population of the different major cities are in a country should be.
 Source: bcg.com
Source: bcg.com
This theoretical guide the rank-size rule predicts a population of 57500 for Quebec City not far off from the actual figure recorded at the time 60000. Using Census data for thousands of US. The population of urban settlements towns cities will be inversely proportional to the rank in the urban Hierarchy. The rank-size rule is a theory. Theoretically there should be.
 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
That means a larger population has a smaller rank in the urban hierarchy. The Rank-Size Rule If all cities in a country are placed in order from the largest to the smallest each one will have a population half the size of the city before it. The Rank-Size Rule If all cities in a country are placed in order from the largest to the smallest each one will have a population half the size of the preceding city. People by the rank of the second-largest city 2. A city that is the largest settlement in a country if it has.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Germany is not a perfect example but it is definitely not a primate city because of the pattern that occurs in city population. That means a larger population has a smaller rank in the urban hierarchy. The population of urban settlements towns cities will be inversely proportional to the rank in the urban Hierarchy. Rank-Size rule in geography UPSC. The Rank Size Rule inspired by Zipfs Law Applied to Distribution of Cities 1935 says if all cities in a country are placed in order from the largest to the smallest each one will have a population 1nth the size of the largest city in the country.
 Source: esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
The Rank-Size Rule. The towns population is derived by dividing the largest citys. The settlements within a defined area are ranked in descending order according to the size of their population. Butler 2005 According to Waugh 2010 the rank size rule is a model that attempts. The major city population is 3547 million and the.
 Source: sphweb.bumc.bu.edu
Source: sphweb.bumc.bu.edu
The population of urban settlements towns cities will be inversely proportional to the rank in the urban Hierarchy. The Rank-Size Rule. Rank Size Rule This is an attempt to find a numerical relationship between population size of settlements within an area such as a country or county Settlements are ranked in descending order of population size with the largest city first. If we estimate this rule for all cities in a region or country and transform everything to a linear form the relationship can be. The rank size rule is an empirical regularity.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The towns population is derived by dividing the largest citys. The major city population is 3547 million and the. The rank-size rule does not imply that the ranking of a city directly relates itself to the population of a city. A larger threshold provides more goods and services a place f. The rank size rule states that the largest city in a given country will have of the population of the largest city in that country.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The Rank-Size Rule. The towns population is derived by dividing the largest citys. Derived from the Central Place Theory that describes the relationship between a citys ranking and its population. Theoretically there should be. The basis for checking the proposed rule is a case-study based on population.
 Source: rockcontent.com
Source: rockcontent.com
The basis for checking the proposed rule is a case-study based on population. The Rank-Size Rule If all cities in a country are placed in order from the largest to the smallest each one will have a population half the size of the preceding city. It replaces the urban rank-size P n P 1 n α by Pn P1 δn1 where Pn is the population size of the n th settlement. Rank-Size rule in geography UPSC. Places we test the hypothesis that the population of a citys second-largest city should be half the size of that it.
 Source: docs.microsoft.com
Source: docs.microsoft.com
The rank size rule is an empirical regularity. The Rank-Size Rule If all cities in a country are placed in order from the largest to the smallest each one will have a population half the size of the preceding city. Rank Size Rule This is an attempt to find a numerical relationship between population size of settlements within an area such as a country or county Settlements are ranked in descending order of population size with the largest city first. Rank 1 Largest City Rank 2 ½ the number of people as Rank 1 city Rank 3 13 the number of people as Rank 1 city. If the largest city has a population 1000000 and we want to know the population of the fourth largest city it will have of the population of the largest city.

The rank-size rule is related to the relative size of cities. For example if a data set consists of items of sizes 5 100 5 and 8 the rank-size distribution is 100 8 5 5 ranks 1 through 4. Also this rule predicts that the larger a citys population is then the fewer number of cities there should be in the surrounding area with a similar population. This is also known as the rank-frequency distribution when the source data are from a frequency distribution. Zipfs law applied to distribution of cities 1935.

Derived from the Central Place Theory that describes the relationship between a citys ranking and its population. The pattern of the rank-size rule was. This is also known as the rank-frequency distribution when the source data are from a frequency distribution. A new rank-size rule for rural settlements is presented. Portable and easy to use Rank Size Rule study sets help you review the information and examples you need to succeed in the time you have available.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title rank size rule example by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






