Your Lagrange multiplier example problems images are available in this site. Lagrange multiplier example problems are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Lagrange multiplier example problems files here. Find and Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for lagrange multiplier example problems images information connected with to the lagrange multiplier example problems topic, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site always gives you suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Lagrange Multiplier Example Problems. Fxyz3xy 3z As youll see the technique is basically the same. Such an example is. Maximizing profits for your business by advertising to as many people as possible comes with. 582 Examples Example 5821 Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the func-tion subject to the given constraints xy z 0and x2 2z2 1.
 Constrained Optimization The Method Of Lagrange Multipliers Advanced Problem Solving Using Maple Applied Mathematics Operations Research Business Analytics From ebrary.net
Constrained Optimization The Method Of Lagrange Multipliers Advanced Problem Solving Using Maple Applied Mathematics Operations Research Business Analytics From ebrary.net
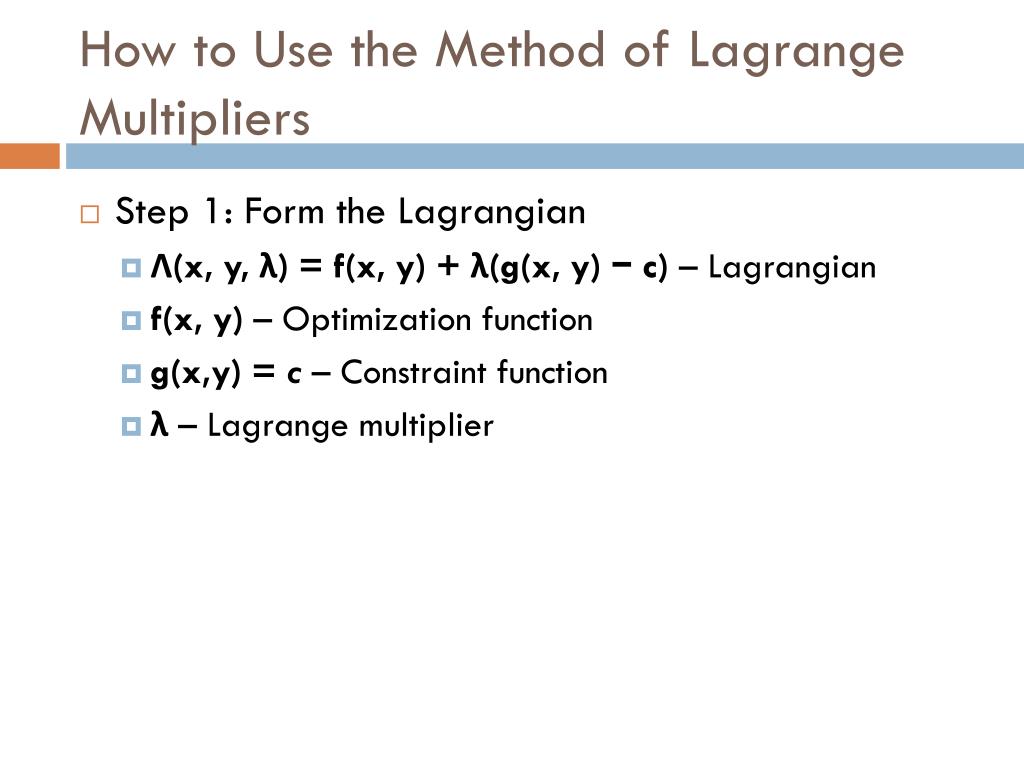
I struggle to come with a visual representation of that. Lagrange Multipliers Lagrange multipliers are a way to solve constrained optimization problems. Plug each one into. The objective function is fx y. Lagrange Multipliers and Constrained Optimization A constrained optimization problem is a problem of the form maximize or minimize the function Fxy subject to the condition gxy 0. Lagrange Multiplier Constraint.
582 Examples Example 5821 Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the func-tion subject to the given constraints xy z 0and x2 2z2 1.
17 hours agoIf a constraint is not active then the solution to the problem found using that constraint would remain at least a local solution if that constraint were removed. Theorem 1391 Lagrange Multipliers. Constrained Optimization using Lagrange Multipliers 5 Figure2shows that. 582 Examples Example 5821 Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the func-tion subject to the given constraints xy z 0and x2 2z2 1. In other words find the critical points of. Lagrange Multipliers and Constrained Optimization A constrained optimization problem is a problem of the form maximize or minimize the function Fxy subject to the condition gxy 0.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Minimize or maximize w fx y z constrained by gx y z c. Now this is exactly the kind of problem that the Lagrange multiplier technique is made for. Theorem 1391 Lagrange Multipliers. Local minima or maxima must occur at a critical point. Were trying to maximize some kind of function and we have a constraint.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Were trying to maximize some kind of function and we have a constraint. Such an example is. The Lagrange multiplier method for solving such problems can now be stated. An Example With Two Lagrange Multipliers In these notes we consider an example of a problem of the form maximize or min-imize fxyz subject to the constraints gxyz 0 and hxyz 0. Xa 1 1 x a 2 2 x a 3 3 λp 1x a 1 λp 2x a 2 λp 3x a 3.
 Source: pdfprof.com
Source: pdfprof.com
On the unit circle. Most real-life functions are subject to constraints. The main difference between the two types of problems is that we will also need to find all the critical points that satisfy the inequality in the constraint and check these in the function when we check the values we found using Lagrange Multipliers. Definition Lagrange method is used for maximizing or minimizing a general function fxyz subject to a constraint or side condition of the form gxyz k. LetRbetheregionintheplaneboundedbythegraphsofy2 4xandy2 4 x.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
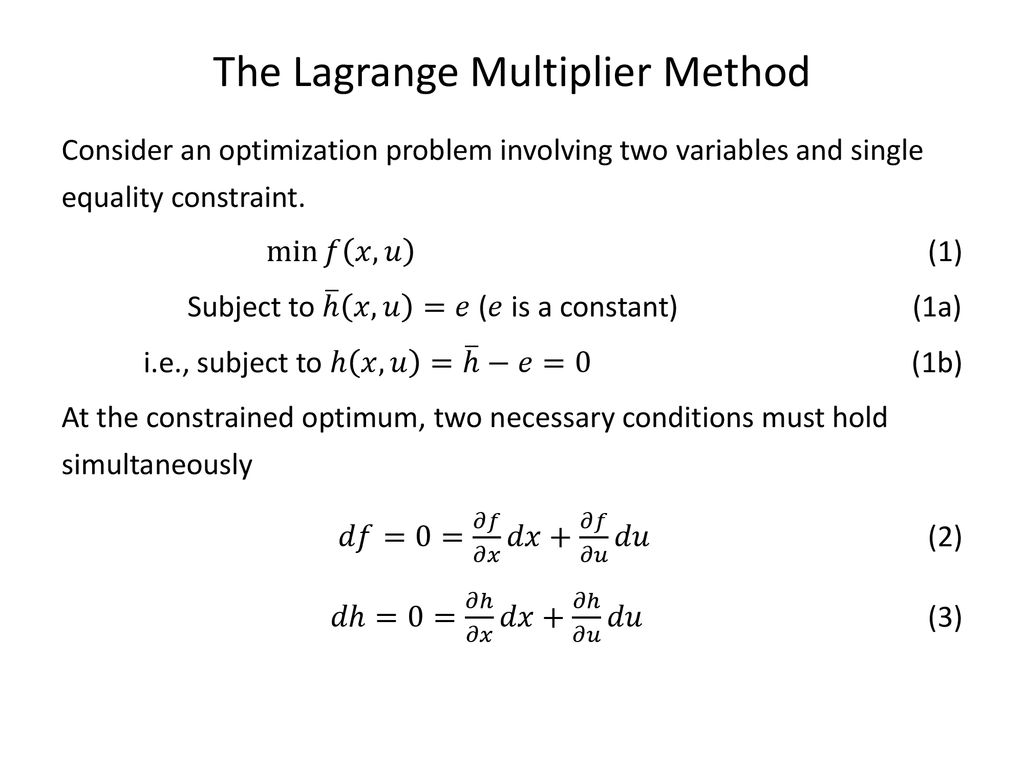
This function is called the Lagrangian and the new variable is referred to as a Lagrange multiplier. 2 ECONOMIC APPLICATIONS OF LAGRANGE MULTIPLIERS If we multiply the first equation by x 1 a 1 the second equation by x 2 2 and the third equation by x 3a 3 then they are all equal. Rf h313i rg h111i rh h2x04zi. Local minima or maxima must occur at a critical point. 582 Examples Example 5821 Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the func-tion subject to the given constraints xy z 0and x2 2z2 1.
 Source: varsitytutors.com
Source: varsitytutors.com
Often this can be done as we have by explicitly combining the equations and then finding critical points. 2 ECONOMIC APPLICATIONS OF LAGRANGE MULTIPLIERS If we multiply the first equation by x 1 a 1 the second equation by x 2 2 and the third equation by x 3a 3 then they are all equal. A Lagrange multiplier is a way to find maximums or minimums of a multivariate function with a constraintThe constraint restricts the function to a smaller subset. 17 hours agoIf a constraint is not active then the solution to the problem found using that constraint would remain at least a local solution if that constraint were removed. Minimize or maximize w fx y z constrained by gx y z c.
 Source: math.stackexchange.com
Source: math.stackexchange.com
Consider each solution which will look something like. Lets work an example to see how these kinds of problems work. Was an applied situation involving maximizing a profit function subject to certain constraintsIn that example the constraints involved a maximum number of golf balls that could be produced and sold in month and a maximum number of advertising hours that could be purchased per month Suppose these were combined into a budgetary constraint such as that. Now this is exactly the kind of problem that the Lagrange multiplier technique is made for. A function is required to be minimized subject to a constraint equation.
 Source: pdfprof.com
Source: pdfprof.com
Lagrange Multiplier Constraint. 1 From two to one In some cases one can solve for y as a function of x and then find the extrema of a one variable function. 582 Examples Example 5821 Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the func-tion subject to the given constraints xy z 0and x2 2z2 1. The constraint x1 does not affect the solution and is called a non-binding or an inactive constraint. 2 ECONOMIC APPLICATIONS OF LAGRANGE MULTIPLIERS If we multiply the first equation by x 1 a 1 the second equation by x 2 2 and the third equation by x 3a 3 then they are all equal.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Minimize or maximize w fx y z constrained by gx y z c. Lagrange Multiplier Constraint. In other words find the critical points of. PracticeProblems for Exam 2Solutions 4. A function is required to be minimized subject to a constraint equation.
 Source: math.stackexchange.com
Source: math.stackexchange.com
For example suppose we want to minimize the function fHx yL x2 y2 subject to the constraint 0 gHx yL xy-2 Here are the constraint surface the contours of f and the solution. In other words find the critical points of. The Lagrange multipliers associated with non-binding. One solution is λ 0 but this forces one of the variables to equal zero and so the utility is zero. Find the maximum and minimum values of f xy 8x22y f x y 8 x 2 2 y subject to the constraint x2 y2 1 x 2 y 2 1.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Constrained Optimization using Lagrange Multipliers 5 Figure2shows that. An Example With Two Lagrange Multipliers In these notes we consider an example of a problem of the form maximize or min-imize fxyz subject to the constraints gxyz 0 and hxyz 0. J Axλ is independent of λat x b the saddle point of J Axλ occurs at a negative value of λ so J Aλ6 0 for any λ0. Find the maximum and minimum values of fx y x 2 x 2y. X y xy 4 x4 y2 R J b Iffxy.
 Source: varsitytutors.com
Source: varsitytutors.com
The objective function is fx y. LetRbetheregionintheplaneboundedbythegraphsofy2 4xandy2 4 x. Minimize or maximize w fx y z constrained by gx y z c. 1 From two to one In some cases one can solve for y as a function of x and then find the extrema of a one variable function. To do so we define the auxiliary function.
 Source: varsitytutors.com
Source: varsitytutors.com
On the unit circle. The Lagrange multipliers associated with non-binding. Discuss some of the lagrange multipliers Learn how to use it Do example problems. Lagrange Multiplier Constraint. Now this is exactly the kind of problem that the Lagrange multiplier technique is made for.

The Lagrange multipliers associated with non-binding. Definition Lagrange method is used for maximizing or minimizing a general function fxyz subject to a constraint or side condition of the form gxyz k. We want to find an extreme value of a function like V x y z subject to a constraint like 1 x 2 y 2 z 2. On the unit circle. The Lagrange multiplier method for solving such problems can now be stated.
 Source: varsitytutors.com
Source: varsitytutors.com
Such problems are called constrained optimization problems. Minimize or maximize w fx y z constrained by gx y z c. Find the maximum and minimum values of f xy 8x22y f x y 8 x 2 2 y subject to the constraint x2 y2 1 x 2 y 2 1. Youre willing to spend 20000 and you wanna make as much money as you can according to this model based on that. Was an applied situation involving maximizing a profit function subject to certain constraintsIn that example the constraints involved a maximum number of golf balls that could be produced and sold in month and a maximum number of advertising hours that could be purchased per month Suppose these were combined into a budgetary constraint such as that.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Section 3-5. To do so we define the auxiliary function. Often this can be done as we have by explicitly combining the equations and then finding critical points. This function is called the Lagrangian and the new variable is referred to as a Lagrange multiplier. Such an example is.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
582 Examples Example 5821 Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the func-tion subject to the given constraints xy z 0and x2 2z2 1. The objective function is fx y. Fxyz3xy 3z As youll see the technique is basically the same. This function is called the Lagrangian and the new variable is referred to as a Lagrange multiplier. To do so we define the auxiliary function.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Lagrange Multipliers Lagrange multipliers are a way to solve constrained optimization problems. Xa 1 1 x a 2 2 x a 3 3 λp 1x a 1 λp 2x a 2 λp 3x a 3. The objective function is fx y. PracticeProblems for Exam 2Solutions 4. It only requires that we look at more equations.
 Source: math.stackexchange.com
Source: math.stackexchange.com
The objective function is fx y. It only requires that we look at more equations. Let fx y and gx y be functions with continuous partial derivatives of all orders and suppose that c is a scalar constant such that gx y 0 for all x y that satisfy the equation gx y c. Plug each one into. The objective function is fx y.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title lagrange multiplier example problems by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






