Your Extraneous conductive parts examples images are ready. Extraneous conductive parts examples are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Extraneous conductive parts examples files here. Get all free images.
If you’re looking for extraneous conductive parts examples pictures information linked to the extraneous conductive parts examples interest, you have visit the right blog. Our site frequently gives you hints for refferencing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Extraneous Conductive Parts Examples. Please Note that if. Rcp UoIb - Ztl where Rcp is the resistance between the conductive part and the MET in ohms Uo is the nominal voltage to Earth in volts Ib is the value of current through the body in amperes that should not be exceeded. Have a look at the definitions of both conductive parts and extraneous conductive parts in the BRB section Lenny has given and the differences will be clearThe key part of the definition of Extraneous conductive parts to lodge on a permanant basis in your grey matter is the bit which saysliable to introduce a potentialusually earthMost of the. Regulation 411312 of BS 76712018 states that.
 Exposed And Extraneous Electrical Conductive Parts The Dangers And The Solutions Youtube From youtube.com
Exposed And Extraneous Electrical Conductive Parts The Dangers And The Solutions Youtube From youtube.com
Metallic service pipes gas oil water steel duct work structural steel. Extraneous conductive part gfËX O ay means a conductive part liable to introduce a potential generally earth. An EXTRANEOUS CONDUCTIVE PART is deemed by some to be anything metallic which doesnt play any part in the electrical installation. Many electricians those new to electrics will ask just what is the difference between an exposed conductive part and an extraneous conductive partIn this. Others say its not EXTRANEOUS if isolated from earth by more than 50Kohms. Explained and Illustrated The IEE Regulations make reference to.
71 f72 IEE Wiring Regulations.
The value may be taken as 30 mA. Or extraneous-conductive-parts and consequently do they require earthing or bonding. Exposed conductive part means the conductive part which can be touched under the provisions of the protection IPXXB and which becomes electrically energized under isolation failure conditions. Every exposed conductive part in order to be adequately protected for indirect contact Fault protection have to be grounded. Others say its not EXTRANEOUS if isolated from earth by more than 50Kohms. Protective equipotential bonding is a method of applying a low impedance path from exposed-conductive-parts to extraneous-conductive-parts to ensure equal potential throughout the installation thus preventing a hazardous potential difference occurring between such parts in the event of a fault.
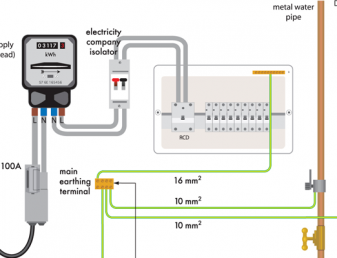 Source: electricalapprentice.co.uk
Source: electricalapprentice.co.uk
A guide to the determination of extraneous-conductive-parts. For example an electrical motor is an exposed conductive part while his metal support is not an exposed conductive part although in the event of a failure both can become live. Protective equipotential bonding is a method of applying a low impedance path from exposed-conductive-parts to extraneous-conductive-parts to ensure equal potential throughout the installation thus preventing a hazardous potential difference occurring between such parts in the event of a fault. A guide to the determination of extraneous-conductive-parts. A guide to the determination of extraneous-conductive-parts.
 Source: voltimum.co.uk
Source: voltimum.co.uk
Exposed conductive part means the conductive part which can be touched under the provisions of the protection IPXXB and which becomes electrically energized under isolation failure conditions. Conductive part not forming a part of the electrical installation and liable to propagate a potential including earth potential. NOTE Examples of other locations include offices social rooms machine-halls workrooms garages and shops. This includes parts under a cover that can be removed without using tools. Every exposed conductive part in order to be adequately protected for indirect contact Fault protection have to be grounded.

NOTE Examples of other locations include offices social rooms machine-halls workrooms garages and shops. Explained and Illustrated The IEE Regulations make reference to. An EXTRANEOUS CONDUCTIVE PART is deemed by some to be anything metallic which doesnt play any part in the electrical installation. The effectiveness of the connection of the extraneous-conductive-parts in the location to the main earthing terminal may be assessed where necessary by the application of Regulation 41522. Regulation 411312 of BS 76712018 states that.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The purpose of main protective bonding is to create an earthed equipotential zone. Others say its not EXTRANEOUS if isolated from earth by more than 50Kohms. Protective equipotential bonding is a method of applying a low impedance path from exposed-conductive-parts to extraneous-conductive-parts to ensure equal potential throughout the installation thus preventing a hazardous potential difference occurring between such parts in the event of a fault. Have a look at the definitions of both conductive parts and extraneous conductive parts in the BRB section Lenny has given and the differences will be clearThe key part of the definition of Extraneous conductive parts to lodge on a permanant basis in your grey matter is the bit which saysliable to introduce a potentialusually earthMost of the. Student training aid re-capping learning on what is the difference between an exposed and extraneous conductive part of an installation.
 Source: voltimum.co.uk
Source: voltimum.co.uk
Residences and other locations which have a conductive connection to the agricultural and horticultural premises by either protective conductors of the same installation or by extraneous-conductive-parts. List examples of extraneous conductive and exposed parts. 71 f72 IEE Wiring Regulations. General matters Mar 14 2008. List THREE examples of extraneous-conductive-parts.
 Source: professional-electrician.com
Source: professional-electrician.com
Others say its not EXTRANEOUS if isolated from earth by more than 50Kohms. Extraneous conductive part gfËX O ay means a conductive part liable to introduce a potential generally earth. All exposed and extraneous conductive parts within this zone are connected to the Main Earth Terminal MET by means of the circuit protective conductors or the main protective bonding conductors. Exposed-Conductive-Part Conductive part of equipment which can be touched and which is not normally live but which may become live under fault conditions. NOTE Examples of other locations include offices social rooms machine-halls workrooms garages and shops.
![]() Source: electricalacademia.com
Source: electricalacademia.com
General matters Mar 14 2008. Extraneous-Conductive-Part A conductive part liable to introduce a potential generally Earth potential and not forming part of the electrical installation. Many electricians those new to electrics will ask just what is the difference between an exposed conductive part and an extraneous conductive partIn this. General matters Mar 14 2008. Exposed conductive part means the conductive part which can be touched under the provisions of the protection IPXXB and which becomes electrically energized under isolation failure conditions.
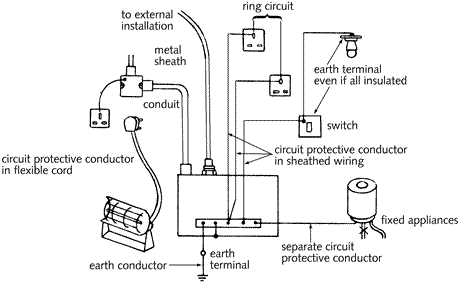 Source: tlc-direct.co.uk
Source: tlc-direct.co.uk
Level 3 Diploma in Electrical Installations Buildings and Structures Unit 305 Worksheet 3. The metallic part can be assumed not to be an extraneous-conductive-part if the following condition is met. 71 f72 IEE Wiring Regulations. Vi All extraneous-conductive-parts of the location are effectively connected to the protective equipotential bonding according to Regulation 411312 NOTE. Conductive part not forming a part of the electrical installation and liable to propagate a potential including earth potential.
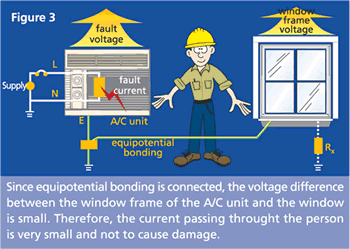 Source: emsd.gov.hk
Source: emsd.gov.hk
Explained and Illustrated The IEE Regulations make reference to. Metallic service pipes gas oil water steel duct work structural steel. We hope that after this discussion you would be more familiar with the determination of extraneous conductive parts and their bonding connection requirements during your design and maintenance work. Switching off for mechanical maintenance The devices for this function should be manually operated and preferably located in the main supply circuit. All exposed and extraneous conductive parts within this zone are connected to the Main Earth Terminal MET by means of the circuit protective conductors or the main protective bonding conductors.
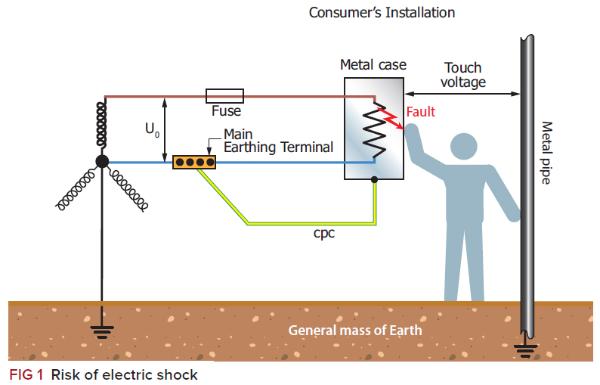 Source: electricalapprentice.co.uk
Source: electricalapprentice.co.uk
An EXTRANEOUS CONDUCTIVE PART is deemed by some to be anything metallic which doesnt play any part in the electrical installation. Residences and other locations which have a conductive connection to the agricultural and horticultural premises by either protective conductors of the same installation or by extraneous-conductive-parts. To provide a means of functional switching and control. Addressing first the question of earthing and whether the cable tray or basket should be earthed electrical equipment such as cables mounted on a metallic support system will normally be equivalent to either a Class I construction for example copper. Conductive part not forming a part of the electrical installation and liable to propagate a potential including earth potential.
 Source: electricalengineeringtoolbox.com
Source: electricalengineeringtoolbox.com
Protective equipotential bonding is a method of applying a low impedance path from exposed-conductive-parts to extraneous-conductive-parts to ensure equal potential throughout the installation thus preventing a hazardous potential difference occurring between such parts in the event of a fault. Conductive part not forming a part of the electrical installation and liable to propagate a potential including earth potential. Level 3 Diploma in Electrical Installations Buildings and Structures Unit 305 Worksheet 3. List examples of extraneous conductive and exposed parts. Rcp UoIb - Ztl where Rcp is the resistance between the conductive part and the MET in ohms Uo is the nominal voltage to Earth in volts Ib is the value of current through the body in amperes that should not be exceeded.

Switching off for mechanical maintenance The devices for this function should be manually operated and preferably located in the main supply circuit. An EXTRANEOUS CONDUCTIVE PART is deemed by some to be anything metallic which doesnt play any part in the electrical installation. Residences and other locations which have a conductive connection to the agricultural and horticultural premises by either protective conductors of the same installation or by extraneous-conductive-parts. Conductive part not forming a part of the electrical installation and liable to propagate a potential including earth potential. Vi All extraneous-conductive-parts of the location are effectively connected to the protective equipotential bonding according to Regulation 411312 NOTE.

This article will consider how to determine that the extraneous-conductive- parts are effectively connected to the MET in a bathroom or shower room. Residences and other locations which have a conductive connection to the agricultural and horticultural premises by either protective conductors of the same installation or by extraneous-conductive-parts. Rcp UoIb - Ztl where Rcp is the resistance between the conductive part and the MET in ohms Uo is the nominal voltage to Earth in volts Ib is the value of current through the body in amperes that should not be exceeded. Exposed conductive part means the conductive part which can be touched under the provisions of the protection IPXXB and which becomes electrically energized under isolation failure conditions. Regulation 411312 of BS 76712018 states that.
 Source: professional-electrician.com
Source: professional-electrician.com
This article will consider how to determine that the extraneous-conductive- parts are effectively connected to the MET in a bathroom or shower room. An EXTRANEOUS CONDUCTIVE PART is deemed by some to be anything metallic which doesnt play any part in the electrical installation. Or extraneous-conductive-parts and consequently do they require earthing or bonding. This includes parts under a cover that can be removed without using tools. Others think this figures too low and raise it etc etc.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Exposed-Conductive-Part Conductive part of equipment which can be touched and which is not normally live but which may become live under fault conditions. IEC 61892-6 Mobile and fixed offshore units Electrical installations Part 6. NOTE Examples of other locations include offices social rooms machine-halls workrooms garages and shops. Vi All extraneous-conductive-parts of the location are effectively connected to the protective equipotential bonding according to Regulation 411312 NOTE. A guide to the determination of extraneous-conductive-parts.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
This includes parts under a cover that can be removed without using tools. Metallic service pipes gas oil water steel duct work structural steel. Switching off for mechanical maintenance The devices for this function should be manually operated and preferably located in the main supply circuit. To provide a means of functional switching and control. Rcp UoIb - Ztl where Rcp is the resistance between the conductive part and the MET in ohms Uo is the nominal voltage to Earth in volts Ib is the value of current through the body in amperes that should not be exceeded.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The value may be taken as 30 mA. Addressing first the question of earthing and whether the cable tray or basket should be earthed electrical equipment such as cables mounted on a metallic support system will normally be equivalent to either a Class I construction for example copper. Rcp UoIb - Ztl where Rcp is the resistance between the conductive part and the MET in ohms Uo is the nominal voltage to Earth in volts Ib is the value of current through the body in amperes that should not be exceeded. NOTE Examples of other locations include offices social rooms machine-halls workrooms garages and shops. Switching off for mechanical maintenance The devices for this function should be manually operated and preferably located in the main supply circuit.

This includes parts under a cover that can be removed without using tools. Rcp UoIb - Ztl where Rcp is the resistance between the conductive part and the MET in ohms Uo is the nominal voltage to Earth in volts Ib is the value of current through the body in amperes that should not be exceeded. Switching off for mechanical maintenance The devices for this function should be manually operated and preferably located in the main supply circuit. We hope that after this discussion you would be more familiar with the determination of extraneous conductive parts and their bonding connection requirements during your design and maintenance work. The effectiveness of the connection of the extraneous-conductive-parts in the location to the main earthing terminal may be assessed where necessary by the application of Regulation 41522.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title extraneous conductive parts examples by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






