Your Examples of plant organs images are available in this site. Examples of plant organs are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Examples of plant organs files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for examples of plant organs images information connected with to the examples of plant organs topic, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
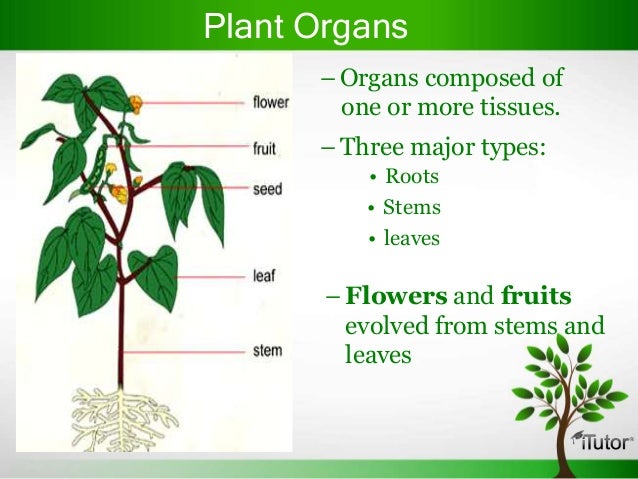
Examples Of Plant Organs. The plant body is an integrated functional unit so the division of a plant into organs is largely conceptual providing a convenient way of approaching plant form and function. Examples of Homologous Organs Forelimbs of Vertebrates Pelvis Present in Snakes Leaves of Cactus Pitcher plant Venus flytrap and poinsettia Mouthparts of Various Insects Ear ossicles of Tetrapods and Bones in Jaw Fish Definition Of Homologous Organs. Its really important for reproduction. They have no problem taking in the sunlight they need for photosynthesis because of how tall they are.
 Plant Development I Tissue Differentiation And Function Organismal Biology From organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu
Plant Development I Tissue Differentiation And Function Organismal Biology From organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu
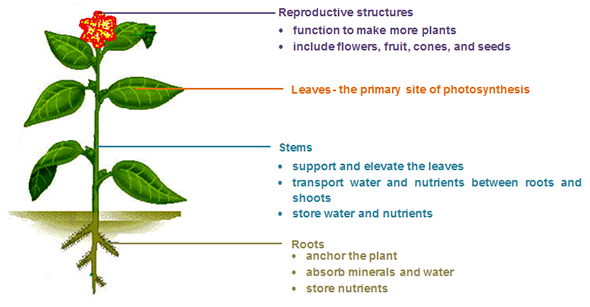
Storage organs may act as perennating organs perennating as in perennial meaning through the year used in the sense of continuing beyond the year and in due course lasting for multiple yearsThese are used by plants to survive adverse periods in the plants life-cycle eg. Their leaves extend well above the surface of the water. Homologous organs are those organs which have the same basic structural design and origin but have different functions. Plants are made up of organs including roots leaves the stem and reproductive organs. Flowers seeds and fruits make up reproductive structures. The flower contains the organs of plant sexual reproduction.
Cell dying-off as well as their mechanical damage results in destruction of intracellular membranes and mixing of the chemical compounds which are separated by membranes in.
Its really important for reproduction. Can your body heal itself from infection. Their leaves extend well above the surface of the water. But both these organs are used for the same function that is the storage of food by the plant making them Analogous Organs. Parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma cells. The chloroplasts within plant cells contain chlorophyll which is what plants use to create energy through photosynthesis.
 Source: blendspace.com
Source: blendspace.com
Cattails are an example of a tall wetland plant that thrives as a result of how high it stands above the waters surface. O2 and excess water are excreted from here. When they dont it. Other plant organs are leaves stems and flowers. Cell dying-off as well as their mechanical damage results in destruction of intracellular membranes and mixing of the chemical compounds which are separated by membranes in.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
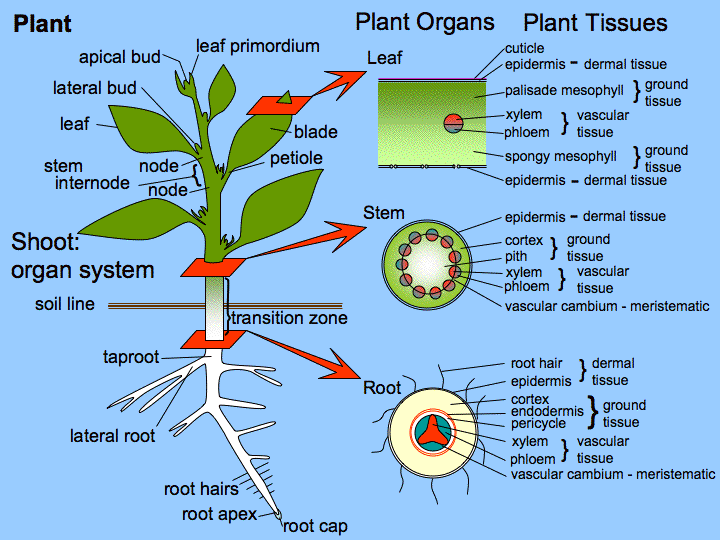
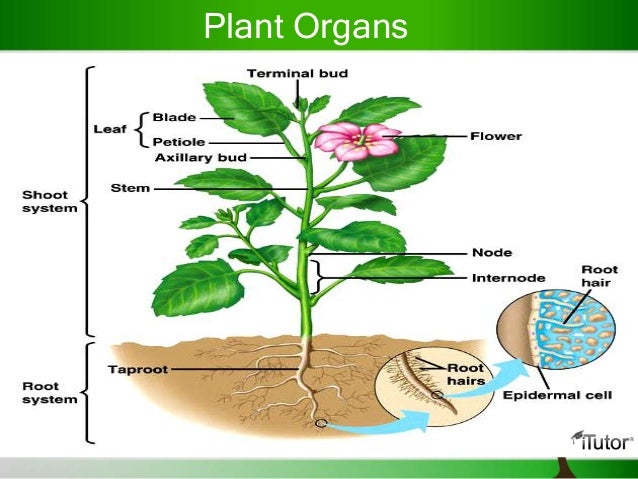
This includes reproductive organs such as stamens and pistils contained in flowers roots stems and leaves. Homologus Organs in plants. Four main plant organs allow the life processes to take place. Plants are multicellular organisms that contain chloroplasts. This includes reproductive organs such as stamens and pistils contained in flowers roots stems and leaves.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Can your body heal itself from infection. What are bones skin and organs examples of. The plant body is an integrated functional unit so the division of a plant into organs is largely conceptual providing a convenient way of approaching plant form and function. Parenchyma cells are the most common. They have two types of transport systems - xylem and.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Typically ranging from three to 10 feet in height these tall plants thrive in muddy water. What Is The Reproductive Organ Of A Plant. The brain heart lungs liver kidneys are a few examples of organs. But both these organs are used for the same function that is the storage of food by the plant making them Analogous Organs. Relationship to perennating organ.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
O2 and excess water are excreted from here. Examples of plant organisms are ferns grass flowers trees and any other multicellular organisms that arent animals. Although we may think of plants as being simpler than animals plants also have organs. Homologous organs are those organs which have the same basic structural design and origin but have different functions. Each organ has its own functions.
 Source: ontrack-media.net
Source: ontrack-media.net
Floating on Water. Parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma cells. They have no problem taking in the sunlight they need for photosynthesis because of how tall they are. The flower contains the organs of plant sexual reproduction. The stem is the organ which holds the leaves upright in the air and facing the light.
 Source: blendspace.com
Source: blendspace.com
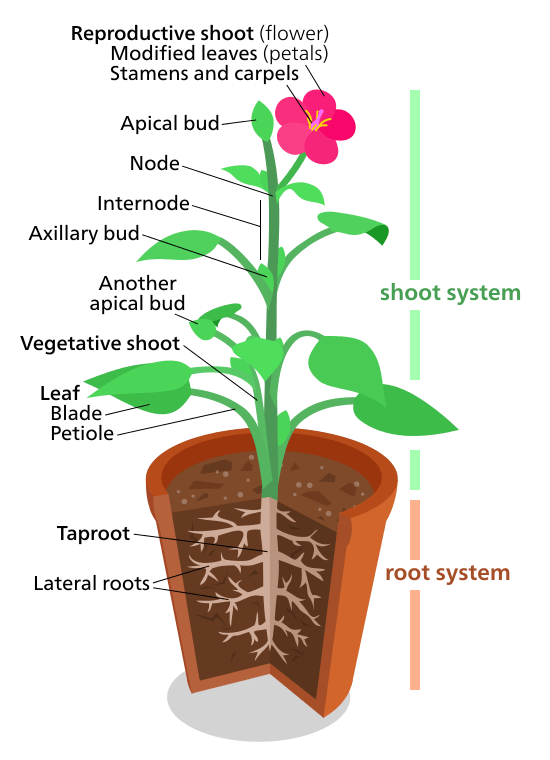
It also gives plants their green color. The root system anchors the plant while absorbing water and minerals from the soil. Plant tissues are of two types. Each plant organ performs a specialized task in the life of the plant. It consists of a pollen sac anther and a long supporting filament.
 Source: www2.estrellamountain.edu
Source: www2.estrellamountain.edu
Examples of Homologous Organs Forelimbs of Vertebrates Pelvis Present in Snakes Leaves of Cactus Pitcher plant Venus flytrap and poinsettia Mouthparts of Various Insects Ear ossicles of Tetrapods and Bones in Jaw Fish Definition Of Homologous Organs. Each plant tissue is specialized for a unique purposeand can be combined with other tissues to create organs such as flowersleavesstems and roots. Homologus Organs in plants. Xylem and Phloem are complex permanent tissues and are found in the vascular bundles in the plants. Leaf the Leaf is a major site of photosynthesis sugars created here are moved to other parts of the plant.
 Source: organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu
Source: organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu
Tracheids and vessels are hollow tube-like structures that help in conducting water and minerals. It consists of a pollen sac anther and a long supporting filament. Each organ has its own functions. Stem Anatomy The stem and other plant organs are primarily made from three simple cell types. Examples of Homologous Organs Forelimbs of Vertebrates Pelvis Present in Snakes Leaves of Cactus Pitcher plant Venus flytrap and poinsettia Mouthparts of Various Insects Ear ossicles of Tetrapods and Bones in Jaw Fish Definition Of Homologous Organs.
 Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
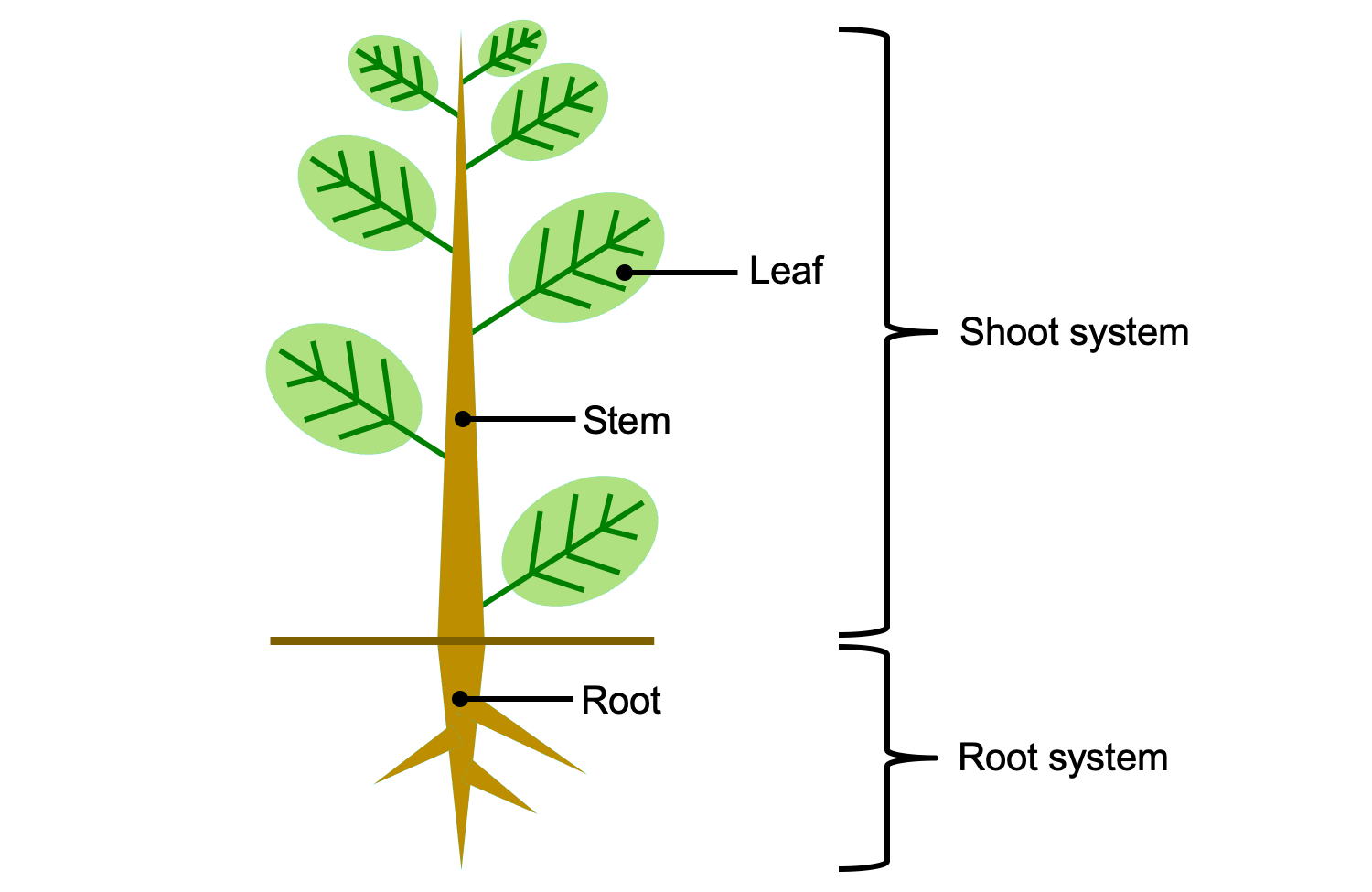
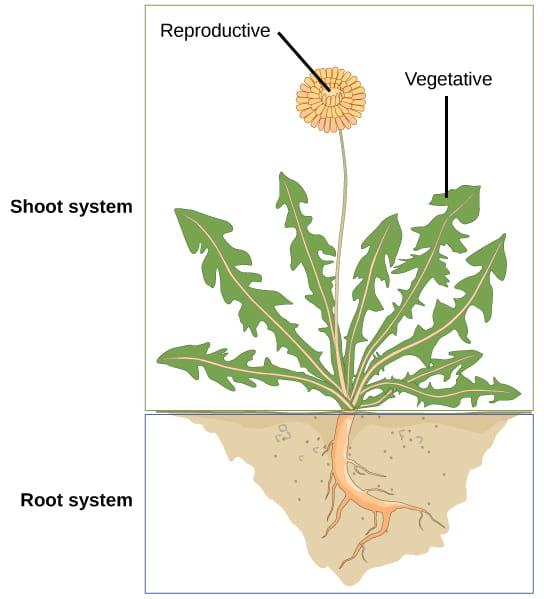
Each of these organs performs specialized tasks such as reproduction absorbing nutrients from the soil and performing photosynthesis. Each plant tissue is specialized for a unique purposeand can be combined with other tissues to create organs such as flowersleavesstems and roots. 8 9 10 Plant organisation The main roles of plant stems and roots are to transport substances around. The stem is the organ which holds the leaves upright in the air and facing the light. Cell dying-off as well as their mechanical damage results in destruction of intracellular membranes and mixing of the chemical compounds which are separated by membranes in.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Examples of plant organs are the root leaves stem seeds etc. Leaf the Leaf is a major site of photosynthesis sugars created here are moved to other parts of the plant. A boundary between stem and leaf is particularly difficult to make so botanists sometimes use the word shoot to refer to the stem and its appendages Esau 1965. What are examples of plant organs. 8 9 10 Plant organisation The main roles of plant stems and roots are to transport substances around.
 Source: organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu
Source: organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu
What are examples of plant organs. 8 9 10 Plant organisation The main roles of plant stems and roots are to transport substances around. Animals The heart is an organ made from muscle and nerve tissue and pumps blood around the body. Its really important for reproduction. Storage organs may act as perennating organs perennating as in perennial meaning through the year used in the sense of continuing beyond the year and in due course lasting for multiple yearsThese are used by plants to survive adverse periods in the plants life-cycle eg.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
O2 and excess water are excreted from here. Although morphologically these two organs may look similar to each other there is a notable difference in their structures. Our bodies can heal almost anything. When they dont it. It consists of a pollen sac anther and a long supporting filament.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The stamen is the male reproductive organ. Plant tissue plant tissue is a collection of similar cells performing an organized function for the plant. Tubers bulbs and trunks of tree species are covered with a layer of dead cells. Tracheids and vessels are hollow tube-like structures that help in conducting water and minerals. What are examples of plant organs.
 Source: mmegias.webs.uvigo.es
Source: mmegias.webs.uvigo.es
The chloroplasts within plant cells contain chlorophyll which is what plants use to create energy through photosynthesis. The stamen is the male reproductive organ. Tracheids and vessels are hollow tube-like structures that help in conducting water and minerals. The root system anchors the plant while absorbing water and minerals from the soil. The leaves of a pitcher plant a Venus fly trap a cactus and a poinsettia are all examples of homology.
 Source: organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu
Source: organismalbio.biosci.gatech.edu
Together the organs of a plant allow it to carry out the seven processes of life. The flower contains the organs of plant sexual reproduction. This includes reproductive organs such as stamens and pistils contained in flowers roots stems and leaves. Each organ has its own functions. Cattails are an example of a tall wetland plant that thrives as a result of how high it stands above the waters surface.
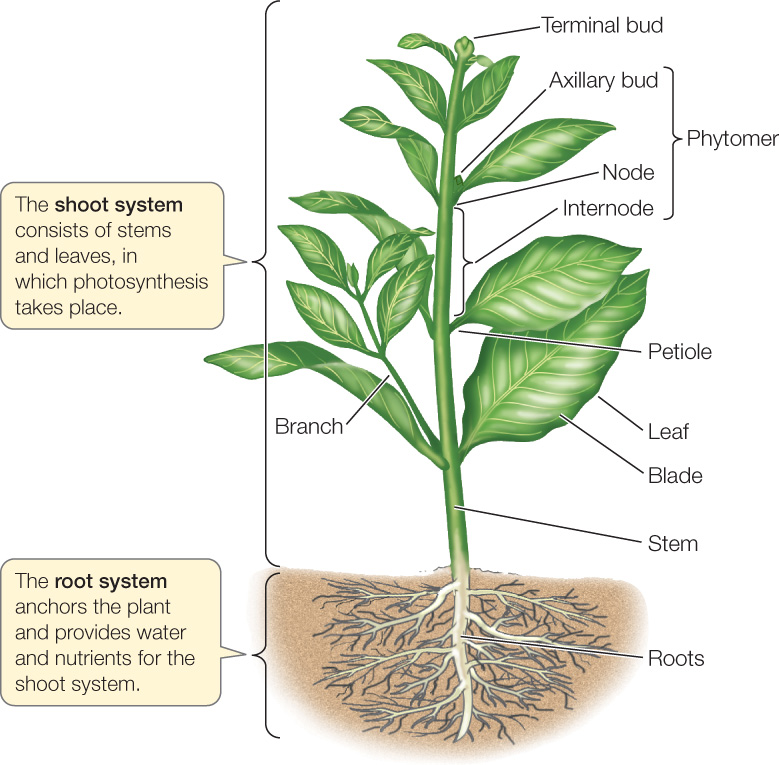 Source: macmillanhighered.com
Source: macmillanhighered.com
Flowers seeds and fruits make up reproductive structures. It consists of a pollen sac anther and a long supporting filament. What are bones skin and organs examples of. 8 9 10 Plant organisation The main roles of plant stems and roots are to transport substances around. Their leaves extend well above the surface of the water.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
What are examples of plant organs. Roots leaves and stems are all vegetative structures. O2 and excess water are excreted from here. When they dont it. The xylem conducts only in one direction ie vertically.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title examples of plant organs by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.