Your Examples of conjugate acid base pairs images are ready in this website. Examples of conjugate acid base pairs are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Examples of conjugate acid base pairs files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re searching for examples of conjugate acid base pairs images information related to the examples of conjugate acid base pairs keyword, you have visit the right blog. Our site frequently gives you hints for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Examples Of Conjugate Acid Base Pairs. 2 with water. OH is. According to this reaction there is a reaction between water and ammonia which in this case are the acid and base respectively because the water donates the protons o. The stronger acid and weaker base form one conjugate pair and the stronger base and weaker acid form another pair.
 Pin On Acid Base Reactions From pinterest.com
Pin On Acid Base Reactions From pinterest.com
The example reaction is between hydrogen fluoride or HF and water. A conjugate pair is always one acid and one base. So hydrogen fluoride is a weak acid and when you put it in water it will dissociate partially. On the other hand a conjugate base is what is left over after an acid has donated a proton during a chemical reaction. All acids have a conjugate base and all bases have a conjugate acid. Were going to introduce the idea of a conjugate acid-base pair using an example reaction.
When it donates a proton a Cl ion is produced and so Cl is the conjugate base.
OH is. In the below picture we provide some examples of conjugated acid-base pairs with their name and formula. For example nitric and sulfuric acid easily donates a proton to water to show acid character. Conjugate acid base pair examples. Acids and bases exist as conjugate acid-base pairsThe term conjugate comes from the Latin stems meaning joined together and refers to things that are joined particularly in pairs such as Brnsted acids and bases. From the list of moleculeion pairs below click on those that are conjugate acid-base pairs.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The example reaction is between hydrogen fluoride or HF and water. All bases have a conjugate acid. Examples of conjugate acids include water base reacting with an acid to form the hydronium ion conjugate acid and ammonia base reacting with an acid to form the ammonium ion conjugate acid. OK you dont have to shout HCl H 2 O H 3 O Cl Here is the one conjugate pair from the first example reaction. When it donates a proton a Cl ion is produced and so Cl is the conjugate base.
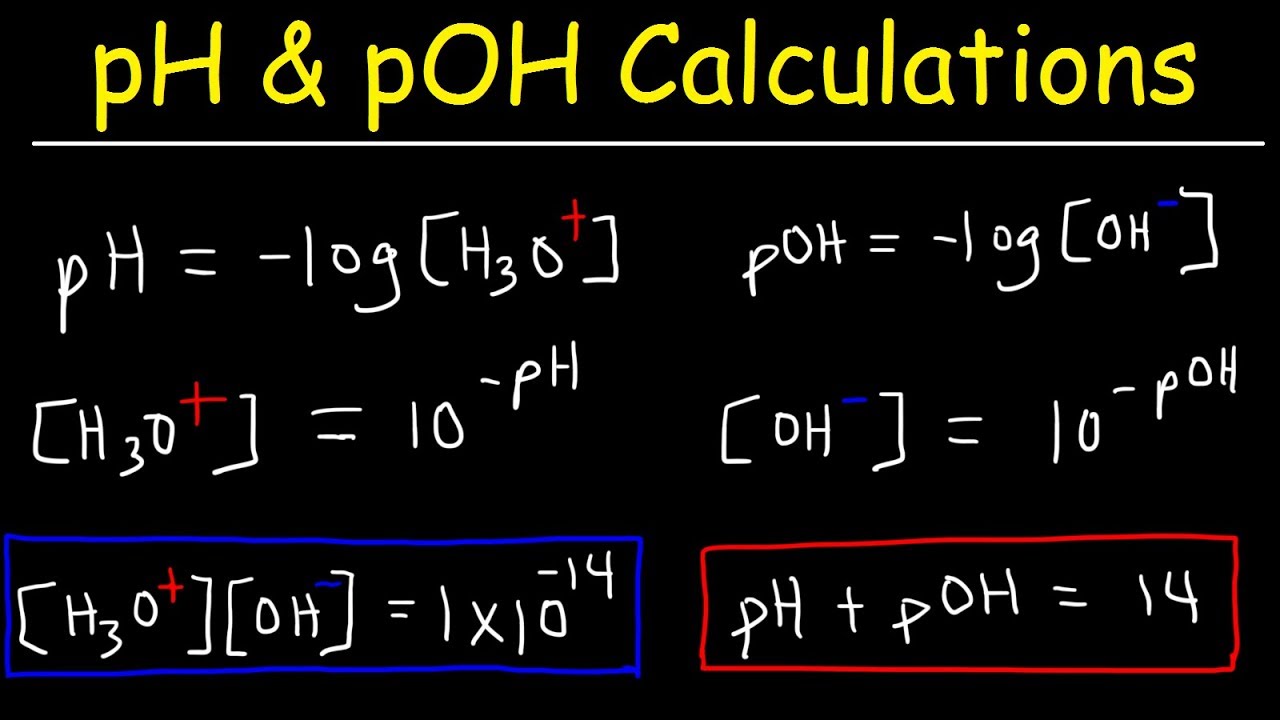 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Write the reaction that occurs and identify the conjugate acid base pairs. Ol OH aq OH aq. Assuming youre referring to a acidconjugate base pair an example would be H2SO4 and HSO4-. All acids have a conjugate base and all bases have a conjugate acid. An example is the base ammonia NH 3 and its conjugate acid the ammonium ion NH 4.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A conjugate pair is always one acid and one base. The conjugates will always be listed on the product side of the reaction. Example PageIndex1. These two are a conjugate pair. HOCN and OCN-are an example of a conjugate acid-base pair.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The basis of buffer action. Buffers can be made from weak acids or base and their salts. All bases have a conjugate acid. TABLE OF CONJUGATE ACID-BASE PAIRS Acid Base K a 25 oC HClO 4 ClO 4 H 2 SO 4 HSO 4 HCl Cl HNO 3 NO 3 H 3 O H 2 O H 2 CrO 4 HCrO 4 18 x 101 H 2 C 2 O 4 oxalic acid HC 2 O 4 590 x 102 H 2 SO 3 SO 2 aq H2 O HSO. H_2SO_4 H_2O HSO_4- H_3O In this example sulfuric acid H_2SO_4 is an acid because it donates H to the water.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
For example if 1221 grams of solid sodium benzoate are dissolved in 100 L 0100 M benzoic acid C6H5COOH pKa 419 solution a buffer with a pH of 419 will result. Every time a Brnsted acid acts as an H -ion donor it forms a conjugate baseImagine a generic acid HA. When this acid donates. We think of them in pairs called conjugate pairs. Acids and bases exist as conjugate acid-base pairsThe term conjugate comes from the Latin stems meaning joined together and refers to things that are joined particularly in pairs such as Brnsted acids and bases.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
HOCN and OCN-are an example of a conjugate acid-base pair. In both cases identify the conjugate acid base pairs. H_2SO_4 H_2O HSO_4- H_3O In this example sulfuric acid H_2SO_4 is an acid because it donates H to the water. When this acid donates. Strong acid forms a weak conjugate base and vice versa.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
O is dissolved in water the solution turns basic from the reaction of the oxide ion O. The example reaction is between hydrogen fluoride or HF and water. When this acid donates. Adding a proton gives CH 3 NH 3 its conjugate acid. A conjugate pair is always one acid and one base.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
O is dissolved in water the solution turns basic from the reaction of the oxide ion O. So Cl is the weak conjugate base of HCl. For example if 1221 grams of solid sodium benzoate are dissolved in 100 L 0100 M benzoic acid C6H5COOH pKa 419 solution a buffer with a pH of 419 will result. The example reaction is between hydrogen fluoride or HF and water. So hydrogen fluoride is a weak acid and when you put it in water it will dissociate partially.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The only difference between the two is a proton H. H 2 SO 4 H HSO 4. Example PageIndex1. So NH 4 is the conjugate acid of NH 3. O is dissolved in water the solution turns basic from the reaction of the oxide ion O.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Members of a conjugate pair differ from each other by the presence or absence of the transferable hydrogen ion. When the acid HA loses a proton it forms a base A-. The conjugate base without the extra proton as the base is in a state to accept a proton. In both cases identify the conjugate acid base pairs. In the below picture we provide some examples of conjugated acid-base pairs with their name and formula.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
When the acid HA loses a proton it forms a base A-. HCl H Cl. HCl and Cl Usually HCl is called an acid and Cl is called its conjugate base but that can be reversed if the context calls for it. When the acid HA loses a proton it forms a base A-. The conjugates will always be listed on the product side of the reaction.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A conjugate base is what you get after removing a. This is most easily seen when they dissociate in water. O is dissolved in water the solution turns basic from the reaction of the oxide ion O. HOCN and OCN-are an example of a conjugate acid-base pair. All acids have a conjugate base and all bases have a conjugate acid.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
HCl H Cl In this reaction HCl is a very strong acid and we know very strong acid always forms the weak conjugate base by donating one proton. On the other hand a conjugate base is what is left over after an acid has donated a proton during a chemical reaction. So NH 4 is the conjugate acid of NH 3. HCl is a strong acid. This is most easily seen when they dissociate in water.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Adding a proton gives CH 3 NH 3 its conjugate acid. A conjugate base comprises one less H atom and one more negative charge than the acid-forming it. It becomes the hydrogen sulfite ion HSO_4- which is the conjugate base of. H_2SO_4 H_2O HSO_4- H_3O In this example sulfuric acid H_2SO_4 is an acid because it donates H to the water. O is dissolved in water the solution turns basic from the reaction of the oxide ion O.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
So NH 4 is the conjugate acid of NH 3. The example reaction is between hydrogen fluoride or HF and water. From the list of moleculeion pairs below click on those that are conjugate acid-base pairs. Any Brønsted acid or base can be thought of as part of a conjugate pair. All acids have a conjugate base.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
D HCO 3. A conjugate acid-base pair contains two compounds that differ only by a hydrogen ion H and a charge of 1. 2 with water. Members of a conjugate pair differ from each other by the presence or absence of the transferable hydrogen ion. An example is the base ammonia NH 3 and its conjugate acid the ammonium ion NH 4.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In both cases identify the conjugate acid base pairs. When lithium oxide Li. When the base A- accepts a proton back again it obviously refoms the acid HA. For example nitric and sulfuric acid easily donates a proton to water to show acid character. When it donates a proton a Cl ion is produced and so Cl is the conjugate base.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
All acids have a conjugate base and all bases have a conjugate acid. We think of them in pairs called conjugate pairs. Some common examples of conjugate acid-base pairs are HClO 4 H ClO 4. A conjugate acid-base pair contains two compounds that differ only by a hydrogen ion H and a charge of 1. Members of a conjugate pair differ from each other by the presence or absence of the transferable hydrogen ion.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title examples of conjugate acid base pairs by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






